Digital disruption touches every facet of our lives, and the banking industry stands at a crucial crossroads. The pandemic has forced an acceleration of digital transformation in banking, shifting it from a growth strategy to an existential imperative. Yet, while many financial institutions have scrambled to adopt new technologies, the true potential of digital transformation extends beyond mere technological upgrades. The key lies not in a digital-first approach, but in brand-driven digital transformation that creates a holistic digital dimension for the financial brand. Such a digital experience resonates emotionally with customers, engenders trust, and builds loyalty through a compelling purpose.
What Digital Transformation in Banking Really Is
Digital transformation in banking usually refers to the comprehensive integration of digital technology into all areas of banking, fundamentally changing how banks operate and deliver value to customers. It involves the use of innovative technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, blockchain, data analytics, and cloud computing to enhance banking services. Digital transformation in banking is driven by the need to improve operational efficiency, and address the competitive pressures from both traditional financial institutions and fintech startups.
However, the real digital transformation in banking transcends technology; it is about crafting a holistic financial brand experience that centers on the human needs and aspirations of customers. Digital transformation, in this sense, involves integrating technology not just to improve efficiency but to cultivate a meaningful and emotionally engaging relationship with customers. Key digital elements, such as AI, blockchain, and data analytics, become enablers of a greater purpose, providing services that reflect genuine empathy and responsibility.
Driving this transformation are shifting customer expectations and fierce competition from both traditional institutions and nimble fintech startups. Based on data from U.S. regional and community financial institutions with $4.4 billion in assets on average, the Alkami report finds that mid-size banks and credit unions more than doubled their investments in digital transformation in fiscal year 2022, to nearly $425,000 per $1 billion in assets, yet the real returns on these investments come only when they are part of a broader, purpose-driven digital branding strategy.
Key challenges of digital transformation in banking include:
- Customer Experience as an Emotional Journey. Digital transformation that places technology in service of empathy and connection enhances not only convenience but also emotional engagement. Banks today must use digital tools to provide a seamless, personalized experience that reflects the values and aspirations of their customers, creating loyalty through meaningful interactions.
- Brand's Purpose at the Core of Customer-Centricity. Successful digital transformation begins by placing a brand's purpose at the heart of customer experience. This involves empowering customers with digital services that support their financial goals, anticipate their needs, and provide transparent, reliable guidance. Digital transformation methodologies alone cannot capture the essence of customer-centricity without this sense of purpose.
- Operational Efficiency with a Human Touch. Automation and digitalization of manual processes reduce operational costs and improve efficiency. Technologies like AI and machine learning are used for tasks ranging from customer service (via chatbots) to risk management and fraud detection, but purpose-driven banks prioritize efficiency that improves human interactions, not just cost metrics. Operational advancements should contribute to creating value for customers, helping them feel that the bank is committed to improving their financial well-being.
- Data as a Tool for Empathy. Banks use big data analytics to gain insights into customer behavior, preferences, and trends. Data analytics offers insights into customer behaviors, but purpose gives meaning to these numbers. Banks that use data to deepen their understanding of customers' unique challenges can tailor digital brand that feels authentic and supportive, rather than purely transaction-driven.
- Innovation with Societal Relevance. Digital transformation encourages the creation of new digital products and services, such as digital wallets, peer-to-peer payments, and blockchain-based solutions. Of course, innovation helps banks stay competitive and meet the evolving needs of their customers, but true innovation in banking considers the societal context. Rather than introducing technology for novelty's sake, digital brands innovate in ways that address real customer and community needs, creating solutions that align with their social and environmental responsibilities.
- Enhanced Security and Trustworthy Compliance. Digital transformation also involves the implementation of advanced cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive data and transactions, but advanced cybersecurity measures are implemented not just for regulatory adherence but to safeguard the emotional bond of trust with customers. Purpose-centered compliance goes beyond meeting regulatory standards; it builds an ethical framework that reassures customers that their digital financial security and privacy are paramount.
- Purposeful Collaboration with Fintech. Collaborating with fintech is no longer about simply accessing new technologies; it’s about creating a cohesive, purpose-driven experience that elevates customer satisfaction and engagement. Banks that purposefully partner with fintech firms can offer innovative solutions tailored to customer needs, providing seamless, meaningful experiences that align with their values. These partnerships are crafted to enhance customer lives and solve real-world problems, resulting in differentiated, customer-centric services that foster deeper relationships and competitive advantage.
- Sustainability and Ethical Commitment to Community Impact. Embedding environmental, social, and governance (ESG) principles into digital transformation reflects a bank's commitment to its broader societal role. Purpose-driven banks integrate sustainable and ethical practices throughout product development, operations, and investments, focusing on creating lasting, positive impacts. This commitment to financial inclusion, reduced carbon footprint, and responsible data usage not only meets customer expectations but also resonates on an emotional level.
- Empowering Employees Through a Purpose-Driven Culture. In a purpose-driven bank, employees are not just equipped with digital skills; they are empowered to contribute to a brand culture that values empathy, purpose, and innovation. This means creating a supportive environment that encourages continuous learning, cross-functional collaboration, and alignment with the bank’s mission to serve customers meaningfully. By investing in training and nurturing a purpose-driven culture, banks can inspire their workforce to connect with customers on a deeper level, empowering service excellence and a shared commitment to fulfilling the brand's purpose. This approach enhances employee engagement, which in turn translates to a more enriching, customer-centered experience.
Why Digital Transformation in Banking Lacks Branding, Not Technology
In recent years, banks have poured substantial resources into digital transformation, rapidly adopting cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence, blockchain, and data analytics. While these advancements are crucial for staying competitive, they often miss a vital component: branding. The most successful transformations in banking are not those that simply leverage technology, but those that seamlessly integrate a powerful brand purpose and create an emotional connection with customers. Here’s why digital transformation in banking needs to shift its focus from technology to branding:
1. Branding Builds Trust, Technology Alone Does Not
Technology can enhance security and streamline transactions, but it doesn’t inherently build trust or loyalty. Customers are not just looking for functionality; they want to know that their bank understands them and aligns with their values. A clear, purpose-driven brand that communicates empathy, reliability, and transparency is essential to winning and retaining customer trust. Banks that invest in branding as part of their digital transformation connect with customers on a deeper level, creating bonds that withstand market fluctuations and competitive pressures.
2. Purpose-Driven Branding Differentiates in a Crowded Market
In a market crowded with traditional banks and fintech disruptors, differentiation is no longer just about product features or faster technology. A purpose-driven brand that reflects customer values stands out in a landscape where many institutions offer similar digital capabilities. A strong brand purpose that goes beyond profits—like promoting financial inclusion or supporting sustainable investments—creates an emotional appeal that technology alone cannot achieve. This differentiation drives loyalty and can turn customers into advocates.
3. Customer Experience Is About Emotion, Not Just Efficiency
Many banks focus on digital transformation to improve operational efficiency and convenience. However, a memorable customer experience involves more than efficiency; it’s about creating positive emotional interactions at every touchpoint. Banks need to leverage technology to enhance their brand experience—crafting interactions that feel personal, responsive, and emotionally resonant. This requires a brand strategy that humanizes digital channels, making customers feel understood and valued, which in turn boosts long-term loyalty.
4. Sustainability and Social Responsibility Drive Modern Brand Expectations
Today’s customers, especially younger generations, expect companies to act responsibly and contribute positively to society. Technology-driven initiatives in sustainability, like reducing carbon footprints or promoting financial education, resonate with customers only when they are part of a cohesive brand narrative. Banks that use digital transformation to further a purpose-driven brand are able to connect authentically with customers who prioritize ethical and sustainable practices, reinforcing loyalty and trust in the brand.
5. Brand Loyalty Leads to Sustainable Growth in Digital Banking
Technology can attract customers with convenience and features, but brand loyalty keeps them coming back. A purpose-driven brand that is integrated into every aspect of digital transformation—from customer interactions to product design—ensures that customers see their bank as more than a transactional entity. Brand loyalty, rooted in a meaningful purpose, offers a sustainable competitive advantage, securing the bank’s position in a fast-evolving digital landscape.
Effective strategy for the digital transformation in banking is the crucial factor determining whether a financial company will lose it all or strengthen its position in the market. A product that doesn't carry any value or benefit to facilitate people's daily lives will not be viewed as a necessity. Global digitalization and the post-pandemic have completely changed the rules of the game in the financial industry. When the primary goal was to make a profit, it was enough with a product, business model and market distribution to ensure the company's success. Now it doesn't work that way anymore, we need empathy and purpose-driven strategy to create a powerful digital brand.
In the digital age, digital branding becomes the main advantage and successful digital products are differentiated by the experience, benefit, and value they provide. That's why in the UXDA we define the digital success formula by adding some very important elements to the traditional operational model. The scale in which a financial business integrates these key factors defines the success potential of its digital financial products.
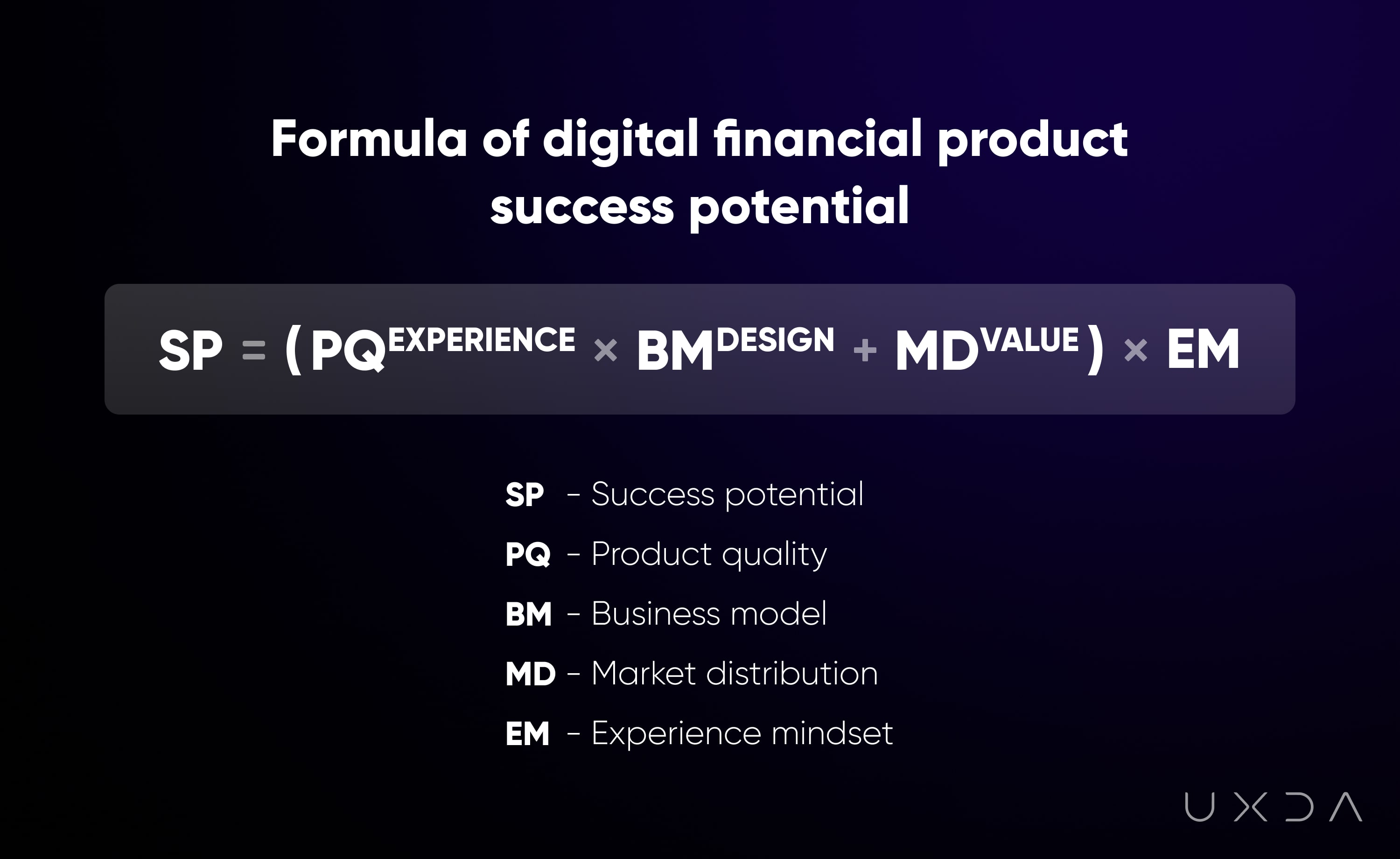
By embracing a purpose-driven strategy as the foundation for digital transformation in banking, banks go beyond simply adopting technology for the sake of efficiency gains or cost savings. Instead, they embrace a holistic approach that integrates technology with their brand purpose and values, focusing on generating positive societal impact, sustainable growth, and responsible practices.
The lack of a digital branding strategy in digital transformation leads to significant disadvantages:
- Fragmented Customer Experience: Banks may leverage separate digital channels to offer services, but without a holistic digital branding approach, these enhancements are fragmented and often miss the mark. True customer experience enhancement comes from ensuring consistency across all digital touch points of the brand to address the specific needs and pain points of customers, which requires a deep sense of empathy and connection with a brand purpose.
- Operational Efficiency Without Direction: Automation and digitalization can reduce operational costs, but if these efficiencies are not aligned with a broader brand purpose and strategy, they can lead to a disconnect between the bank and its customers. Efficiency for efficiency’s sake does not create value.
- Data-Driven Decisions Lacking Insight: Big data analytics can offer insights into customer behavior, but without a purpose to guide these insights, banks risk focusing on the wrong metrics. Purpose-driven data analytics look beyond the numbers to understand the human stories behind them bridging the emotional bond between customers and financial brand.
- Innovation Without Meaning: Developing new digital products and services is crucial, but innovation without purpose can result in solutions in search of problems. Purpose-driven innovation starts with a clear understanding of the societal and customer issues that need addressing by the brand.
Technology as a Financial Brand Amplifier, Not a Replacement
Future-ready banks recognize that their greatest brand assets are not just their reputation, history, financial services or technological innovations, but the people they serve. By prioritizing empathy and design in their digital transformation strategy, banks can create meaningful, consistent and authentic user experiences that align with their customers' needs and values. This approach will not only secure their brand place in the future of banking but also contribute to a more inclusive, accessible, and human-centered financial ecosystem.
In a world of rapid digital transformation, where AI, blockchain, and data analytics are becoming standard, what truly sets a financial institution apart isn’t its tech stack but its brand identity. Successful digital transformation in banking should enhance, not eclipse, the unique brand values that have cultivated customer trust over decades. Here’s how banks can ensure technology serves as a tool to strengthen their brand, not overshadow it:
1. Reaffirming Purpose Amidst a Digital Race
The focus on digital transformation has intensified competition among banks to adopt the latest technologies. While technology is essential for operational efficiency and customer convenience, it’s not the core of a bank’s identity. A bank’s brand is built on values like trust, reliability, and customer service—values that technology should reinforce, not replace. Banks need to keep a clear sight of their purpose: to serve customers’ financial well-being, empower their dreams, and foster trust in every interaction. In the digital age, this purpose should shine through every digital channel and service.
Example: Instead of promoting a new AI-powered customer service tool simply for its tech appeal, banks could showcase how it enables customers to manage their finances more effectively, positioning it as part of their commitment to making banking simpler and more supportive.
2. Don’t Just Chase Trends—Invest in Brand-Enhancing Technology
It’s tempting to jump on the latest tech trends to stay competitive, but each technological investment should reflect the bank’s brand values and serve customer needs. For instance, mobile banking apps, digital wallets, and AI-based financial planning tools all present opportunities to deepen brand connections. When customers use these services, the experience should feel consistent with the bank’s identity and foster an emotional connection, not just tick a box on the latest trend.
Example: If a bank prides itself on being family-oriented, it could develop digital tools that encourage shared financial planning for families or offer features that support financial education for children. Such technology would directly reflect and amplify the bank’s brand values.
3. Create a Customer-Centric Experience, Not a Tech Showcase
Digital transformation often focuses on automation, speed, and efficiency, but these alone don’t make a brand memorable. Customers don’t just want quick transactions; they want meaningful, humanized experiences. Banks should design digital services with the customer’s journey and emotional needs in mind, not merely to showcase technology. Building customer-centric experiences means asking what customers truly need and designing services that feel personal, supportive, and aligned with the brand’s commitment to its users.
Example: Instead of a generic chatbot, a bank known for its personal touch could develop an AI assistant with a conversational tone that reflects the brand’s warmth and approachability, making digital interactions feel less transactional and more human.
4. Branding Through Ethical and Purpose-Driven Technology
Today’s customers are savvy and expect brands to stand for something meaningful. In banking, digital transformation offers an opportunity to demonstrate a commitment to ethics and responsibility. This means not only protecting customer data through robust cybersecurity but also using data responsibly to enhance the customer experience. Purpose-driven technology investments—like tools that promote financial literacy, ethical lending practices, or environmental sustainability—can amplify the brand’s values and foster a deeper sense of loyalty.
Example: A bank that positions itself as eco-friendly could adopt digital tools to measure and offset the carbon footprint of its transactions, or offer products that encourage sustainable investments. This would align the technology with the brand’s social responsibility and appeal to environmentally-conscious customers.
5. Personalized Service as a Brand Differentiator in Digital Spaces
Digital transformation doesn’t mean sacrificing personal service. In fact, digital tools should be used to enhance personalization, allowing banks to tailor products, advice, and offers to each customer’s unique needs. Personalization, powered by data but delivered with brand sensitivity, can make each customer interaction feel bespoke and meaningful. This level of care goes beyond automation and directly supports a bank’s commitment to understanding and meeting individual customer needs, reinforcing brand loyalty in a personalized digital experience.
Example: A bank known for supporting small businesses could use digital insights to offer business clients personalized financial products or alerts for potential savings, making clients feel understood and valued in a way that deepens their trust in the bank’s brand.
6. Leveraging Fintech Partnerships to Strengthen Brand Identity
Partnerships with fintech companies can be a powerful way to expand digital capabilities, but banks should carefully select fintech partners that align with their brand values. Rather than diluting their identity, collaborations should reinforce the bank’s commitment to customer needs and foster brand loyalty. A fintech partnership should feel like a natural extension of the brand’s values, offering innovative solutions that resonate with what the bank stands for.
Example: A community-focused bank might partner with a fintech that specializes in local business financing, positioning itself as an advocate for local economic growth and building brand equity with community-minded customers.
7. Empowering Employees to Reflect the Brand Digitally
Digital transformation isn’t just about customer-facing tech; it’s also about empowering employees to deliver the brand experience digitally. Equipping employees with digital skills and fostering a culture of empathy and customer-centricity is essential. Employees who understand and embody the brand’s values can use digital tools to provide exceptional service that is both efficient and reflective of the brand’s identity. This internal transformation helps ensure that the brand experience is consistent across all channels.
Example: A community bank that values personal connections could empower its relationship managers with digital tools to offer remote, personalized consultations, ensuring that customers feel valued even in a digital interaction.
8. Using Data Responsibly to Build Trust, Not Just Efficiency
In the age of big data, digital transformation often involves collecting and analyzing vast amounts of customer information. However, banks must prioritize responsible data use to build trust, not just to enhance efficiency. Transparent communication around data use and a commitment to privacy are essential to maintaining a trustworthy brand image. Responsible data practices demonstrate respect for customer privacy and reinforce the brand’s dedication to ethical standards.
Example: Instead of aggressively marketing based on data analytics, a bank could offer opt-in personalized insights that empower customers to make informed financial decisions, showing respect for their data privacy and increasing trust.
9. Creating a Seamless Brand Experience Across Digital and Physical Channels
In a digitally transforming world, customers often interact with banks across multiple channels, from mobile apps to in-branch visits. Ensuring a seamless brand experience across digital and physical interactions is essential for reinforcing brand identity. Every touchpoint, whether online or in-person, should consistently reflect the bank’s values and personality, creating a cohesive brand journey that resonates with customers and strengthens their loyalty.
Example: A bank that emphasizes simplicity and transparency should reflect these values in both its digital interfaces and physical branches, creating a uniform experience that reassures customers of the brand’s commitment to clarity and ease.
10. Ensuring Brand Consistency in Digital Product Design
Finally, every digital product and service should be designed with the bank’s brand identity in mind. A strong brand identity creates an emotional connection with customers, and every digital interaction is an opportunity to reinforce that connection. Digital products should be thoughtfully designed to reflect the brand’s aesthetic, tone, and values, ensuring that customers recognize the brand’s unique essence at every touchpoint.
Example: If a bank’s brand identity revolves around sophistication and elegance, its logo, brand identity, digital communications, mobile app and online platforms should feature tailor-made, refined, minimalistic design that reflect this authentic identity, creating a cohesive and recognizable brand experience.
Conclusion: Importance of Digital Transformation to Shift from Tech-First to Brand-First
Digital transformation offers immense opportunities for banks to innovate and remain competitive. However, as technology takes center stage, banks must remember that digital tools should amplify their brand’s purpose and values, not obscure them. When technology serves as a vehicle to reinforce brand identity, it creates authentic, lasting connections with customers.
The future of digital transformation in banking lies in creating a brand that resonates with customers on an emotional level, ensures trust, and reflects shared values. Banks that embrace a brand-first approach to digital transformation will not only stand out in a competitive market but will also build lasting loyalty, making their brand a trusted part of customers' lives.
If we accept that technology is merely a tool and not an end goal in itself, then the real measure of success will be the strength and longevity of the relationships that financial brands build with their clients. This digital evolution is fundamentally about people—about understanding their needs, preferences, and behaviors in a rapidly changing digital landscape.
By adopting a brand-first approach to digital transformation, banks can harness the power of technology to create meaningful, emotionally resonant experiences that differentiate them in the marketplace. After all, in the race to digitalize, it’s not just about being technologically advanced—it’s about being a bank that customers trust, remember, and choose time and time again.
In the past nine years, the exclusive financial UX agency UXDA has completed over 150 digital financial app design transformations for financial brands in 37 countries. Explore our examples of financial app design transformation that exceeds expectations and creates an emotional connection through a stunning UX design by UXDA:
Get UXDA Research-Based White Paper "How to Win the Hearts of Digital Customers":
 If you want to create next-gen financial products to receive an exceptional competitive advantage in the digital age, contact us! With the power of financial UX design, we can help you turn your business into a beloved financial brand with a strong emotional connection with your clients, resulting in success, demand, and long-term customer loyalty.
If you want to create next-gen financial products to receive an exceptional competitive advantage in the digital age, contact us! With the power of financial UX design, we can help you turn your business into a beloved financial brand with a strong emotional connection with your clients, resulting in success, demand, and long-term customer loyalty.
- E-mail us at info@theuxda.com
- Chat with us in Whatsapp
- Send a direct message to UXDA's CEO Alex Kreger on Linkedin